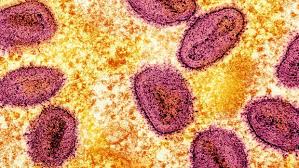
The mpox virus, once known as monkeypox, has made a comeback with a new, more severe version dubbed Clade 1b.https://www.cbc.ca/news/health/mpox-global-emergency-explainer- https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/cvg35w27gzno. This variety has been spreading quickly in parts of Africa, particularly the Democratic Republic of Congo, and has now been found in several other countries, including Sweden and Germany.https://www.cbc.ca/news/health/mpox-global-emergency-explainer- https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/cvg35w27gznohttps://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/international/global-trends/newer-mpox-strain-subvariant-clade-ib-poses-bigger-threat-to-girls-young-women-spreading-fast-congo-burundi-symptoms/articleshows.
The new variation has a greater fatality rate than earlier strains, with up to 10% of cases resulting in death (source: https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/cvg35w27gzno).
- Enhanced Transmission: This variation spreads faster through intimate physical contact, including sexual contact.https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/cvg35w27gznohttps://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/international/global-trends/newer-mpox-strain-subvariant-clade-ib-poses-bigger-threat-to-girls-young-women-spreading-fast-congo-burundi-symptoms/articleshow.
- Vulnerable Populations: According to recent studies, girls and young women may be more vulnerable to this new strain.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has labeled this epidemic as a global health emergency, highlighting